Circumcision - Female Genital Mutilation
Circumcision - Female Genital Mutilation (FGM)

World Health Organization
Fact sheet N241, June 2000
Female genital mutilation
What is female genital mutilation?
Female genital mutilation (FGM), often referred to as 'female circumcision', comprises all procedures involving partial or total removal of the external female genitalia or other injury to the female genital organs whether for cultural, religious or other non-therapeutic reasons. There are different types of female genital mutilation known to be practised today. They include:
- Type I - excision of the prepuce, with or without excision of part or all of the clitoris;
- Type II - excision of the clitoris with partial or total excision of the labia minora;
- Type III - excision of part or all of the external genitalia and stitching/narrowing of the vaginal opening (infibulation);
- Type IV - pricking, piercing or incising of the clitoris and/or labia; stretching of the clitoris and/or labia; cauterization by burning of the clitoris and surrounding tissue;
- scraping of tissue surrounding the vaginal orifice (angurya cuts) or cutting of the vagina (gishiri cuts);
- introduction of corrosive substances or herbs into the vagina to cause bleeding or for the purpose of tightening or narrowing it; and any other procedure that falls under the definition given above.
The most common type of female genital mutilation is excision of the clitoris and the labia minora, accounting for up to 80% of all cases; the most extreme form is infibulation, which constitutes about 15% of all procedures.
Health consequences of FGM
The immediate and long-term health consequences of female genital mutilation vary according to the type and severity of the procedure performed.
Immediate complications include severe pain, shock, haemorrhage, urine retention, ulceration of the genital region and injury to adjacent tissue. Haemorrhage and infection can cause death.
More recently, concern has arisen about possible transmission of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) due to the use of one instrument in multiple operations, but this has not been the subject of detailed research.
Long term consequences include cysts and abscesses, keloid scar formation, damage to the urethra resulting in urinary incontinence, dyspareunia (painful sexual intercourse) and sexual dysfunction and difficulties with childbirth.
Psychosexual and psychological health: Genital mutilation may leave a lasting mark on the life and mind of the woman who has undergone it. In the longer term, women may suffer feelings of incompleteness, anxiety and depression.
Who performs FGM, at what age and for what reasons?
In cultures where it is an accepted norm, female genital mutilation is practiced by followers of all religious beliefs as well as animists and non believers. FGM is usually performed by a female traditional practitioner with crude instruments and without anaesthetic. Among the more affluent in society it may be performed in a health care facility by qualified health personnel. WHO is opposed to medicalization of all the types of female genital mutilation.
The age at which female genital mutilation is performed varies from area to area. It is performed on infants a few days old, female children and adolescents and, occasionally, on mature women.
The reasons given by families for having FGM performed include:
- psychosexual reasons: reduction or elimination of the sensitive tissue of the outer genitalia, particularly the clitoris, in order to attenuate sexual desire in the female, maintain chastity and virginity before marriage and fidelity during marriage, and increase male sexual pleasure;
- sociological reasons: identification with the cultural heritage, initiation of girls into womanhood, social integration and the maintenance of social cohesion;
- hygiene and aesthetic reasons: the external female genitalia are considered dirty and unsightly and are to be removed to promote hygiene and provide aesthetic appeal;
- myths: enhancement of fertility and promotion of child survival;
- religious reasons: Some Muslim communities, however, practise FGM in the belief that it is demanded by the Islamic faith. The practice, however, predates Islam.
Prevalence and distribution of FGM
Most of the girls and women who have undergone genital mutilation live in 28 African countries, although some live in Asia and the Middle East. They are also increasingly found in Europe, Australia, Canada and the USA, primarily among immigrants from these countries. In Canada, FGM is a criminal offensive, whether or not the procedure was performed in Canada or another country to a Canadian female.
Today, the number of girls and women who have been undergone female genital mutilation is estimated at between 100 and 140 million. It is estimated that each year, a further 2 million girls are at risk of undergoing FGM.
Current WHO activities related to FGM
- Advocacy and policy development
A joint WHO/UNICEF/UNFPA policy statement on FGM and a Regional Plan to Accelerate the Elimination of FGM were published to promote policy development and action at the global, regional, and national level. Several countries where FGM is a traditional practice are now developing national plans of action based on the FGM prevention strategy proposed by WHO.
- Research and development
A major objective of WHO's work on FGM is to generate knowledge, test interventions to promote the elimination of FGM. Research protocols on FGM have been developed with a network of collaborating research institutions as well as biomedical and social science researchers with linkages to appropriate communities. WHO has reviewed programming approaches for the prevention of FGM in countries and has organized training for community workers to strengthen their effectiveness in promoting prevention of FGM at the grassroots level.
- Development of training materials and training for health care providers
WHO has developed training materials for integrating the prevention of FGM into nursing, midwifery and medical curricula as well as for in-service training of health workers. Evidence based training workshops, to raise the awareness of health workers and to solicit their active involvement as advocates against FGM, have also been developed for nurses and midwives in the African and Eastern Mediterranean region.
For further information, journalists can contact :
WHO Press Spokesperson and Coordinator, Spokesperson's Office,
WHO HQ, Geneva, Switzerland / Tel +41 22 791 4458/2599 / Fax +41 22 791 4858 / e-Mail:
inf@who.int

Pediatricians turn away from circumcision
The United States is the only country that routinely circumcises baby boys for non-religious reasons
CNN, U.S.A.
March 1, 1999
ATLANTA (CNN) -- American pediatricians are turning away from the practice of routine circumcision, concluding that doctors have no good medical reason to perform the procedure.
The United States is the only country in the world that routinely removes the foreskins of infant boys. Critics of circumcision got additional ammunition Monday from the American Academy of Pediatrics, a leading medical organization.
The academy concluded the benefits "are not compelling enough" for circumcision to be routinely administered.
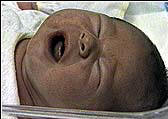
A newborn winces in pain after a circumcision
Monday's statement, published in the March edition of the journal Pediatrics, was the academy's first in 10 years on the practice. But in recent years, medical societies in Canada, Britain and Australia have come out in opposition to routine circumcision.
Critics have long contended that removing the foreskin from the penis is traumatic, medically unnecessary and may reduce sexual pleasure later in life. As one critic, Dr. George Denniston, put it: "Who are we to question mother nature?"
Canadian researchers, whose study was published in this week's Journal of the American Medical Association, studied the heart rates and crying patterns of babies during different stages of circumcision.
In fact, in the study they found the babies suffered so much trauma that they stopped the study part way through.
The results were so compelling that they took the unusual step of stopping the study before it was scheduled to end rather than subjecting any Read More ..bies to circumcision.
One baby stopped breathing for 25 seconds from the trauma of having part of his foreskin severed. Read More ..
![]()
Baby Dies of Herpes in Ritual Circumcision By Orthodox Jews
ABC News, U.S.A., by Susan Donaldson James, March 12, 2012
New York City is investigating the death last September of a baby who contracted herpes after a "ritual circumcision with oral suction," in an ultra-Orthodox Jewish ceremony known in Hebrew as metzitzah b'peh.
The district attorney's office in Kings County Brooklyn is investigating the death of the 2-week-old baby at Maimonides Hospital, but would not disclose the name of the mohel or whether there would be a prosecution.
The 5,000-year-old religious practice is seen primarily in ultra-Orthodox and some orthodox communities and has caused an alarm among city health officials. In 2003 and 2004, three babies, including a set of twins, were infected with Type 1 herpes; the cases were linked to circumcision, and one boy died.
The mohel who performed the procedures, Yitzchok Fischer, was later banned from doing circumcisions, according to The New York Times. It is not known if he was involved in this recent death.
"It's certainly not something any of us recommend in the modern infection-control era," said Dr. William Schaffner, chair of preventive medicine at Vanderbilt University.
"This is a ritual of historic Abraham that's come down through the ages, and now it has met modern science," he said. "It was never a good idea, and there is a better way to do this." (The modern Jewish community uses a sterile aspiration device to clean the wound in a circumcision.)
In the 2004 death and the more recent one, a mohel infected the penile wounds with Type 1 herpes I (HSV-1), which affects the mouth and throat. It is different from Type 2 or genital herpes (HSV-2), which is a sexually transmitted disease and can cause deadly infections when a newborn passes through an infected birth canal.
Neonatal herpes is "almost always" a fatal infection, according to Schaffner. "It's a bad virus. [Infants] have no immunity and so it's a very serious illness. Now we have another death -- an unnecessary, incredibly tragic death."
![]()
Circumcision Botched by Jewish Father Results in Conviction for Aggravated Assault
The Canadian Press
Dec. 22, 2011
VANCOUVER - A B.C. man who performed a botched circumcision on his four-year-old son on the kitchen floor of his home has lost an appeal of his conviction and been found guilty of a more serious charge.
The B.C. Court of Appeal has stayed the man's conviction for criminal negligence causing bodily harm and convicted him of aggravated assault.
Court heard the boy was born premature at only 2.5 pounds and could not be circumcised at the time, nor did his parents request it.
South Korean Doctors
Male circumcision based on myths and misinformation
Peak age of circumcision of males in Korea is 12 years old!
UTIs are rare

"Of every 1,000 boys who are circumcised 2 will be admitted to hospital for a urinary tract infection (UTI) before they are one year old."
"Of every 1,000 boys who are not circumcised 7 will be admitted to hospital for a UTI before they are one year old. "

Sur 1 000 garçons circoncis 2 seront hospitalisés en raison d'une infection urinaire avant l'âge d'un an.
Sur 1 000 garçons non circoncis 7 seront hospitalisés par suite d'une infection urinaire avant l'âge d'un an.
CanadianCRC editor:
Anyone who states that urinary tract infections are common among newborn baby boys, and therefore
advocates that the genital mutilation of boys ( male circumcision) will stop urinary tract infections, is a liar or misinformed.
Besides, urinary tract infections are entirely treatable.
Men's News Daily Online
Commentary on the David Reimer botched circumcision / gender changed case
When Feminist Dogma Met Dr. Mengele
CanadianCRC editor's Note: Reminder about our policy: Many sides of an issue are expressed in articles on this website. Many articles contain points of view which should be heard but are not the position of the Canadian Children's Rights Council.
"..Circumcision May CAUSE Urinary Tract Infection"
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are rare, and mainly occur in the first year of life. They are several times Read More .. common in girls than boys (but of course surgery is never considered for girls).
They are painful, and women's experience of them is a powerful inducement to have sons circumcised, if they imagine that this will protect them. In fact, a significant proportion of boys contract UTIs even though they are circumcised. A study in Israel found they mainly occurred in girls at four months, but in boys soon after they were circumcised.... Now an Australian study suggests circumcision may cause urinary problems. Read More ..
2003 British Medical Association Statement Against Circumcision
The BMA does not believe that parental preference alone constitutes sufficient grounds for performing a surgical procedure on a child unable to express his own view. . . . Parental preference must be weighed in terms of the child's interests. . . . The BMA considers that the evidence concerning health benefit from non-therapeutic circumcision is insufficient for this alone to be a justification for doing it. . . . Some doctors may wish to not perform circumcisions for reasons of conscience. Doctors are under no obligation to comply with a request to circumcise a child. Read More ..

